Running a small business is like navigating a complex maze while juggling chainsaws. There is always something that needs your focus be it the balance sheets, the sales campaigns, and others. Nevertheless, sometimes it is easier to solve the urgent problems instead of focusing on the important aspects, such as design, which is an important factor that can affect the success of the business.
To some extent, UX vs UI design are like two sides of a ship’s wheel – both are distinct elements of website design, but both have equal importance and are inextricably related. UI is the outlook of the Website and can ensure that all the image-oriented parts of the Website are well designed or developed.
On a different note, UX is the mastermind of the whole process keeping in mind that users have to follow a logical and engaging route while navigating through the website. A beautiful UI but a very poor UX is something that will make users abandon the website and on the other extreme, a great UX that comes with a very bad UI is something that will just leave the users fully confused.
There is a subtle moment when UX and UI design are perfectly integrated, and people are getting viewable and engaging websites. Consequently, the businesses not only get more visitors to their site but also turn them into customers, this re-emphasizes the need to have both UI & UX on the website .
Whereas UI is concerned with elements such as the button, colors and layouts, the UX penetrates to know how the user feels when he is with the site. And it is not even about making visuals; it is about making everything look like one homogenous unit that web design company Florida can definitely help you with.
As stated by Forrester, by optimizing the website I can improve the conversion rate by up to 200%, while an optimized UX will take that figure to as much as 400%. The symbiosis of UX and UI design is the key to generate visually pleasant and usable websites and to increase customers’ pleasure as well as company’s effectiveness.
So, let us understand both essential concepts for web design:
Essential Concepts For Web Design
User Interface (UI):
UI, or User Interface, is concerned only with the appearance of structures and the arrangement of their web sites. While UX is all about the experience your users have, UI can be translated as the graphic design of your website: the buttons, icons, spacing, fonts, colors and anything you click on.
It’s like the front door of the actual shop: it attracts attention and makes your handling of it as simple and pleasant as possible.
For example, a good UI provides for the proper positioning of buttons on a device, the appropriate choice of colors that reflect on the brand identity and readability of the fonts. The aim is to achieve an obvious, ergonomic and beautiful design.
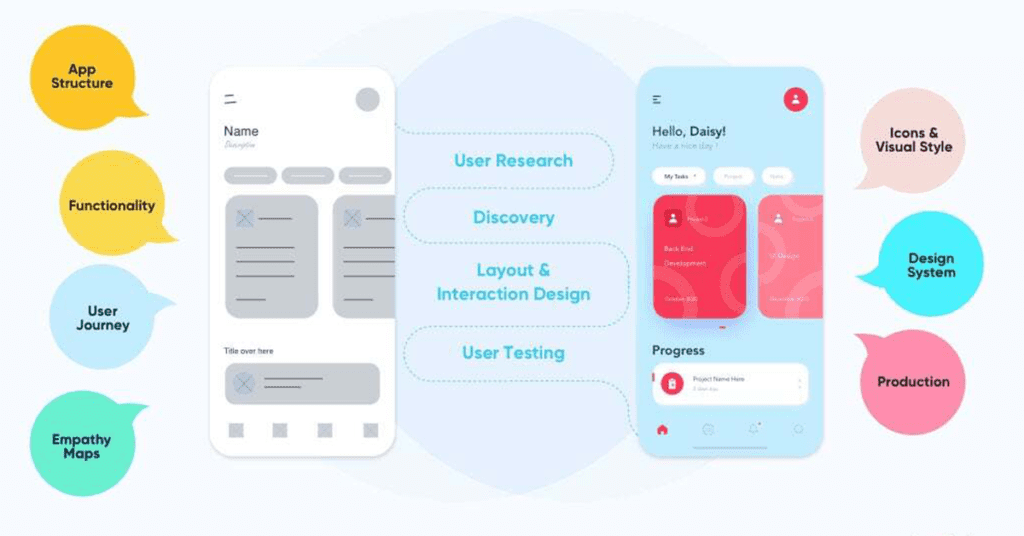
User Experience (UX):
On the other hand, UX or User Experience goes further to the emotions a user goes through when using the website. That’s why it’s not necessary what it looks like anymore, rather what it does and how user-friendly it is. UX includes anything starting from the ease with which information can be located to the ease of making a purchase.
So, regard UX as the entire experience to do with that well-mastered shop that already has the outstanding looks – how easy it was to locate what we were in search of, how friendly the attendants were, and overall satisfaction level. Good UX always ensures that the user does not only come to the site but also would like to be there and even spend some more time.
UX Vs UI Design And Its Effect On Business
We all know that creating a high-quality UX and UI design is not just about aesthetics but bringing substantial business value. According to research, investing in UX can have a ROI for every dollar invested and this can be as high as $100, meaning that the percentage return of investment is 9,900%. Also, companies that practice customer experience design get to gain improved customer retention levels of 17%, increase in the derived revenues from cross selling and up selling by 22%, and finally, a 25% reduced customer acquisition costs.
Larger companies can afford these loses since they deal with high volumes of business while small businesses need to give importance to UX and UI designs. A good UX/UI website design agency or an offshore software development company can definitely streamline the process and can go a long way in enhancing your business profit due to increased customer satisfaction, more conversion rates and hence more revenues.
Difference between UX/UI Designer and Web designer:
Web Designer, UX/UI Designer are all significant for designing a Website, Mobile Application, or any other digital product, but they have a different area of work. Here’s a breakdown of their main differences:Here’s a breakdown of their main differences:
- Web Designer
Focus: Aesthetics of the websites.
Key Responsibilities:
- Web designing is about designing the format of the web site and the layout and the appearance of the web site.
- Making sure that the site is good looking, easy to navigate and aligned to the corporate image of a brand.
- Incorporates use of HTML, CSS, and at times JavaScript to create designs and make them become real.
- May manage, for instance, the responsive design to make sure that the website functions appropriately within devices.
Skills: Graphic design, typography, color theory and some HTML/CSS, knowledge of Adobe XD, Figma, Sketch.
- User Interface (UI) Designer
Focus: The appearance of the buttons, icons and other interactive or graphical items of a digital product.
Key Responsibilities:
- Creating all graphics that the user operates like buttons, icons, sliders, and forms.
- Making sure that the interface has the right looks which is an identity of the brand.
- Working with other UX designers to make sure that the design of the product is not only good to the eyes but also very easy to work on the interface.
- Designing and developing design systems, and style guides that would be used through the whole course of the product.
Skills: Graphic design, interaction design, understanding of types, colours, context with design tools adobe sketch, figma, Adobe XD and how interfaces work.
3. User Experience (UX) Designer
Focus: The impression that a user has with a specific product or service when the user interface has been applied.
Key Responsibilities:
- Comparing and selecting the appropriate method to face the user’s necessities, behaviors and problems.
- Sustaining guidelines such as the use of user personas, journey maps and wireframes in the course of designing.
- Having a more cross-disciplinary approach pooling the knowledge of designers with different skills and incorporating feedback from consumers during the production of prototypes that are used in usability testing.
- Guaranteeing that the product is easy to use, understandable and meets the client’s needs to the maximum extent.
Skills: Knowledge of users, their needs, and behavior; ability to structure the information, as well as design and tutorial skills; the usage of designing tools such as Figma, Adobe XD, Axure, or InVision; knowledge about human psychology.
How Do UX and UI Design Work Together?
If UX and UI design are different in web design, they are correlated and cannot exist on their own. While it makes sense to want to impress visitors with a beautiful and well-crafted UI, with no actual usability behind the visuals, those visitors will not hesitate to abandon the site in exasperation. On the other hand, a modern website with good usability but bad appealing aesthetics will not even interest the users.
For instance let us take an example of an E-commerce site selling online products. A good UI will enhance the visibility of the product images and enhance the circulation of the site clicks while good UX will ensure that searching for a particular product, adding the product to cart and checking out is a smooth and hassle free process.
In one way, UX and UI design ensures the thorough process of browsing to purchasing is an enjoyable one.
Why Is Combining UI/UX Design The Smart Move To Invest In?
In the modern society, potential clients’ initial contact is mostly through the website of the organization they need to engage with. As much as you would not wish to walk into a store with circuits messed up in such a way that you do not know which way to look, the same way, the users do not wish to be directed through a website that has been designed in such a haphazard manner.
Investing in both can pay off big time, and here’s why:
- First Impressions Matter
Just recall how many times you approached a site that seemed to be left in oblivion or did not seem to feature a user-friendly interface. I bet you did not hang around for more than five minutes, did you? It’s because, in just 50ms, or the fraction of a second that it takes for users to blink their eyes, their impressions about a website are often formed and a significant number of these impressions are formed based on the UI design. Properly designed, effective, and minimalistic interface design can help users establish a trust towards your brand as soon as they encounter it.
- Boosts Conversion Rates
The more sophisticated the UI, the more chances you have to improve website conversion rates by 200%, better UX can cause conversion rates up to 400%. What this means is that every time you redesign your site to make it more attractive, easy to use, more customers are created from your visitors. Think about increasing your productivity, let’s say, two- or fourfold, just because you want to make your design look different.
- Enhances Customer Satisfaction
When the web designing looks more professional , it makes the user experience more comfortable and interesting. This means that the happy clients will be the returning ones hence impacting the customer revisitation rate. Customers will also be more willing to introduce other people to your site ensuring that more potential customers will approach the site on their own.
- Reduces cost in long run
Quality improvement in users’ interface and users’ experience is cheaper when initially considered in an investment. How? In that it eliminated the need for constant fixes and redesign of structures and products. A website, which was designed badly, is usually updated more often due to complaints of the users of the site or other problems with site operations. Such problems are avoided by having a good design from the beginning and therefore cuts down on website maintenanace cost and time used.
- Improves SEO Performance
Search engines, Google in the lead, are only getting more intelligent, and they care more about the users than ever. Properly developed seo friendly website and having a very good user’s experience not only helps in getting more attention from the users but in addition enhances the rankings of the website in search engines. Unfortunately, it also indicates that a generous investment of time and effort into good UX and UI design will also rank your site higher and send you more organic traffic.
- Builds Brand Loyalty
This idea cuts across all areas of operation for a business; people remember experience rather than a product. Whenever customers have a good experience, they will be able to associate your brand with that experience and come again for more. PwC’s study showed that 32% of customers are ready to cut their ties with a favourite brand after a single negative experience. Good and functional user interface and user experience design keep users engaged and building a good relationship with the website or application.
- Stand Out From the Crowd
When there are so many brands in the market, it will be wise to set yourself apart. This is especially so in the case of your competitors offering similar products or even services to your organization’s; a good user experience can help to create that major difference. Another reason is if the customer finds that your site is far easier to navigate and a lot better looking than the competition then you can be assured that you’ll be winning their custom.
Breaking Down UX Vs UI Design Best Practices
Now, let’s take a closer look at some of the aspects and guidelines that can help you create an attractive and effective UI/UX web design.
1. User Research and Personas
Audience analysis is among the first critical activities that are performed in the course of UX design. Who are your users? What matters to them, what they like and dislike, and what challenges or problems do they face? This information is gathered through user research, and once that is done, you can develop user personas, hypothetical individuals who embody your target demographic. These personas direct the designing process, and, therefore, your website will suit the requirements of the users.
Best Practice:
Surveys, interviews, and usability testing allow the creation of a user perspective to gather information about them. Apply it to create precise and well-elaborated personas that would be at the base of your design.
2. Information Architecture (IA)
Information architecture (IA) is the process of categorizing and arranging the content of your website in such a manner that the user gets what he/ she wants. The IA organizes your website for your benefit and makes understanding the structure of your online platform easier, thus driving your website visitors’ cognitive load down.
Best Practice:
Best Practice: Card sorting and tree testing are the most valuable methods for designing an effective structure for the website’s content. Make sure your website navigation is well-defined, with labels that are simple and clear to your users.
3. Wireframing and Prototyping
Wireframes are rapid prototypes of your web site architecture. It is important if you are getting a layout designed for your site because they give a detail of how the various components of the site will appear on the layout. Prototyping goes a step ahead with the layout in that it provides a means of simulating an actual site where one will get to experience the flow and more of the user interface before coding commences.
Best Practice:
It’s best to design simple web page layouts that highlight all crucial pages of the website: navigation menus, call-to-action buttons, and content blocks. To put into practice design solutions developed, it is necessary to use actual software, such as Adobe XD or Figma, to design clickable prototypes that will let a true audience try the product.
4. Visual Design Principles
For most of the website design, especially in the context of UI design, visual elements are helpful in crafting an interactivity as well as well-balanced visual ui. But visual design is not just about how things look – it is also about the way through which they are perceived by the users and how it enhances their experience.
Best Practice:
Incorporate contrast, alignment, and other aspects of visual UI design to make your website appealing and easy to navigate. Select the colors that represent your brand and stick to the typography that is easy to comprehend.
5. Responsive Design
Today, the majority of the website visitors use mobile devices: mobile-first approach is the thing of the present. A responsive website design is one where the layout and the objects used in the website are adjusted to suit the dimension of the devices accessing it.
Best Practice:
Use other methodologies like the flexing grid that comprises images that are fluid on the different classes of devices, the media queries for different classes of devices.
Final Thoughts
Finally, UX and UI design are a match made in heaven where web design is concerned. Together, they design and develop sites that are pleasing to the eyes as well as easy and fun to navigate.
It is this complementarity that is most effective – just imagine that 88% of Internet users are ready to abandon the site after a bad purchase. This reveals how important it is to get both UX and UI design in the right perspective.
A well-design interface attracts people’s eyes, but a well-designed, fluid, and easy-to-use interface draws people’s inputs. Combining the best of UI, which is a site’s visual design and gorgeous appearance, with the best of UX, related to site usability and return on investment, businesses can create websites that are not only beautiful to look at but also functional and effective for their needs.
